Top 5 Cyber Security Risks for Your Business
The importance of cyber security is growing day by day thanks to the rapidly advancing technology.
The ongoing cyber security incidents and more importantly the impact of those are driving organizations towards recognizing cyber security component as one of the core business requirements.
Believe it or not, but just by scrolling down newsfeed you can see data breaches (and other sorts of cyber security incidents) if not on a daily, then surely on a weekly basis. Those not only cause enormous financial losses but can also affect people’s privacy!
Remember Equifax data breach in 2017 that exposed personal data on hundreds of millions of people?
It was announced that the credit bureau must pay $700 million with the U.S. and its states.
You are probably wondering: What are the weaknesses for most businesses when it comes to cyber security and how to protect against the threats?
Here’s the good news: we are here to discuss the top 5 cyber security risks for your business!
Insider Threat [does not sleep!]
Please note: the term ‘Insider Threat’ is referred to only rogue insiders in this post.

“When there is no enemy within, the enemies outside cannot hurt you.” (W. Churchill)
Don’t get us wrong: we do NOT mean that your boss, employees or colleagues are enemies. Let’s look deeper and replace the word ‘enemy’ with ‘threat’.
Seems like fiction, but just a few decades ago the world was not shaken by such terms as cyber crime or cyber attack, but Churchill did realize that nothing can do more damage than the threat that comes from within.
Again, Churchill, who was very unlikely to be a cybersecurity expert (although we can’t be 100% sure), realized that, so should YOU.
Here is why we believe that insider threat is one of the top cyber security risks for your business:

But that’s just part of the story…
In fact, insider threat may come not only from employees, but also from contractors, suppliers or service providers. In other words, from anyone who may have direct physical and/or remote access to your physical/virtual assets and infrastructure.
“Insider threat may come not only from employees, but also from contractors, suppliers or service providers.”
We bet there is a high probability that you have never thought of that, haven’t you?
Why does this matter?
Unlike the unsuspecting employees who may accidentally click on the link or open an email attachment from unknown address without realizing it may harm the organization, rogue insiders have a clear purpose for their actions.
Possible outcomes? Let’s look at a couple of real-life examples below:
1. Anthony Levandowski Case
You might have heard this one: Anthony Levandowski, a former employee of what is now called Waymo (Google’s project for driverless cars), allegedly copied thousands of confidential documents with the proprietary technology pertaining to Waymo before his resignation.
Anthony then founded his own company – Otto Motors. Waymo’s intellectual property was then presumably sold to Uber, which bought Otto Motors.
As a result, Law suit between Waymo and Uber settled In February of 2018. According to Reuters, Uber paid “$245 million worth of its own shares to Alphabet Inc’s Waymo self-driving vehicle unit.”
2. Christopher Grupe Case
No wonder that Waymo-Uber Case was highly publicized.
But let’s look at the Grupe’s example to see another side of the insider threat (our apologies – it will be quite a lot of text). According to the US Department of Justice press release:
“…from September 2013 until December 2015, Grupe was employed as an IT professional by Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), a transcontinental railroad company headquartered in Alberta, Canada…
On Dec. 15, 2015, following a 12-day suspension, Grupe was notified by CPR management that he was going to be fired due to insubordination.
However, at his request, Grupe was instead allowed to resign, effective that same day. In his resignation letter, Grupe indicated that he would return all company property, including his laptop, remote access device, and access badges, to the CPR office.
As proven at trial, on Dec. 17, 2015, before returning his laptop and remote access device, Grupe used both to gain access to the CPR network’s core “switches” – high-powered computers through which critical data in the CPR network flowed.
Once inside, Grupe strategically deleted files, removed administrative-level accounts, and changed passwords on the remaining administrative-level accounts, thereby locking CPR out of these network switches. Grupe then attempted to conceal his activity by wiping the laptop’s hard drive before returning it to CPR.”
Sounds ridiculous, doesn’t it? (we mean the situation, not the amount of text).
In the end, it led to Lots of headache for Canadian Pacific Railway and $30,000 of financial losses to cover for the destroyed IT infrastructure.
What does this mean to you and your company?
Here’s the deal (or the bitter truth): you cannot avoid the risk of insider threat.
The good news: you can mitigate it, and here are a few ways how:
- On-Boarding and Off-Boarding Best Practices (background checks, managing access);
- Access Control and Identity Management (access to sensitive information is role-based – principle of least privilege);
- Acceptable Use Best Practices (how to handle sensitive information/assets);
- Cyber Awareness Training (you should not forget that employees are the greatest asset);
- Supplier On-Boarding and Off-Boarding Best Practices (same as you would do above when hiring a new employee).
In our experience, all of these should be captured in company policies that will be communicated, enforced and monitored to manage the organizational cybersecurity stability.
This is what we at Genieall also have gone through as part of ISO 27001 certification. It is tough – no doubt about it.
Be careful! The Phishing season has started!

We won’t be wrong if we say that everyone (ourselves included), who is using or has used an email or phone (or any other connected device), has faced an attempt to have any piece of our PII (Personal Identifiable Information) compromised, or phished.
You or your family/friends/colleagues have most likely received a call/text or an email at least once supposedly from:
- Bank (‘account compromised or confirm your information’)
- Friends or relatives in need (who ‘got into trouble or accident’)
- Service that you use (delivery/Netflix)
- Service provider (similar to a bank above)
- Revenue Officers (‘get more tax return’ or ‘you didn’t pay taxes’)
- Microsoft Tech Support (‘scanned you computer and found a virus’)
- College or university you attended (‘confirm your information’)
“Yes, I agree it is terrible, but how does this relate to my company?”
Well, here’s the deal: as much as any of the phishing techniques can be used to steal PII or any credentials for further use, any of those techniques (including emails and calls from the above-mentioned list) can be and are often used to trick employees or business owners into sharing the company’s login credentials.
But wait there is more! Phishing emails can contain malicious attachments that once opened, will load malicious programs (e.g. malware – covered right after) onto the victim’s machine.
Why does this matter?
Here’s the deal: phishing is one of the top cyber security risks for your business.
You may not agree with or believe us (though we really hope you do), but check out the following stats:
1. Retruster collected and presented more phishing stats:

What does this mean to you and your company?
Don’t worry, you and your company are not the first and not the last to be a phishing target.
However, unlike those who fell the victim of phishing scams, your organization has an advantage. You will be prepared for phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques.
“Your organization can avoid being a victim of phishing attack.”
Another bitter truth: your company cannot avoid phishing attacks.
Another good news: your organization can avoid being a victim of phishing attack.
Here is how:
- Install anti-phishing protection enabling phishing scanning and preventing the members of the network from accessing phishing websites;
- Develop cyber security awareness framework and perform regular sessions internally;
- Check suspicious emails, link or attachments on credibility;
- Report suspicious activities.
ATTENTION! Malware

Cyber evolution never ends!
You see, past threats and tech advancements have led to a relatively new cyber creature – Malware – one of the top cyber security risks for your business. This hazard infects approximately one third of the computers and leads to trillions of dollars in losses each year worldwide.
Sounds impressive, does not it?!
To know how to defend against an enemy, we need to know him in face!
Simply put, the term “malware” is referred to most of the MALicious softWARE installed on computer which has a capability to self-replicate over a network.
Let’s look at some main malware types a bit closer:
- Ransomware means Ransom malware that encrypts all the data on the computer and demands ransom for the decryption key.
- Trojan is aimed at getting control over your device.It manipulates the computer, intentionally nudging a person to run it eagerly while hiding behind a malicious program.
- Worm is a malicious software which spreads independently from infected computer to others. It destroys device memory that results in decreased computer performance.
- Spyware works like a detective which monitors your activity during the device usage. Through this program hackers can follow all your actions such as view emails, watch you through the web camera and other means.
Why does this matter?
“Ooops, your files have been encrypted!”.
No doubt about it, this is the last thing that you want to see on your screen. However, this is what you can find on your display after computer/system infection.
Think about it: present malicious programs are more sophisticated than their predecessors.
Just couple decades ago, worms or viruses were considered as an annoying thing which pops up on a display and distracts from work. Today, it’s a money-making industry which develops ways to steal user information in exchange for money.
But that’s just part of the story.
According to the recent statistics, there have been 2,396,830 new malware types developed during the first half of 2018 alone!
Can you imagine the enormous number of malicious programs living in the internet nowadays? We can’t…
Mostly, they are spread through the web which makes it difficult to identify them.
“There have been 2,396,830 new malware types developed during the first half of 2018 alone!”
For example, ransomware can now be delivered with the MS Office documents (used by virtually every organization). Once the document is opened, the whole system is infected, and the information is automatically encrypted.
And, as if it was not enough, here is a real-life example:
WannaCry: Cyber plague of the 21st century
This attack is considered to be one of the most terrifying and far-reaching for many industries. In just a few days, this malware infected more than 200,000 devices in 150 counties!
Healthcare centers and factories (and even government bodies) were under attack. That resulted in encrypted information, decentralization of factory systems, and threatened the efficiency of massive production systems. Not to forget huge financial implications.
What does this mean to you and your company?
You were probably wondering: if my organization is small (in size and/or revenue), then why do I need to care about this?
To save some time answering this question, please take a look at these stats:
According to 2019 Verizon Data Breach investigations Report, 43% of data breaches involved small businesses.
But wait, there is more: per VIPRE, 66% of SMBs would either go out of business completely, or be forced to shut down for at least a day following a cyber breach.
While the threats are silently waiting along the information superhighway, the development of cybersecurity framework is still in the end users’ hands.
The safety means vary with the size of organization:
- Small businesses with a small number of computers: Introduce antivirus and anti-spyware software on every device.
- Businesses with 10-20 computers: Contemplate a security suite. It helps to manage a central secure software.
- Businesses with more than 20 computers: The best way is to use enterprise-level tools which centralize administration on the higher level with important updates and provide more advanced security tools for bigger companies.
Cryptojacking: ‘Revolutionary Cash Cow’

“Bitcoin is a technological tour de force.” – Bill Gates, Co-founder of Microsoft.
Digital money… we all know them.
We bet that there is a good chance that you know about the cryptocurrency too (thanks to the media covering the booming growth for the last few years).
Bitcoin, Ethereum and hundreds of other cryptocurrencies that got into the news and got popularity across the globe.
Well, you’ve heard about it, so have cyber criminals.
Here comes a new cyber security risk for your business: cryptojacking – the technological “Cash Cow”!
“Cryptomining has risen by 8500 % around the globe in 2017.”
It is an illegal invasion in network/system with a purpose to mine cryptocurrency through the malicious software or just a script. It can happen through the malware download or through the infected webpage in the target’s internet browser.
Why does this matter?
It’s all about the costs!
According to the recent Symantec report, cryptomining has risen by 8500 % around the globe in 2017 which highlights the increasing threat of becoming a next target!
“During the past year, an astronomical rise in cryptocurrency values triggered a crypto jacking gold rush with cyber criminals attempting to cash in on a volatile market,” emphasizes the article.
Simply stated: the increase in value of the currency makes it a desirable target for criminals. Here is an example how much approximately a coin-mining program makes per month:
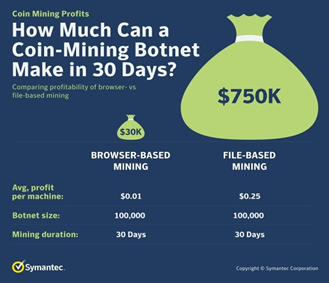
Think about how much money one criminal can make through the coin-mining botnet just in 30 days and why more and more hackers turn to this type of cyber attack!
Here are a few several real-world cryptojacking examples to show the increasing threat of this hacking method:
1. GitHub (2018)
“In March, Avast Software reported that cryptojackers were using GitHub as a host for cryptomining malware. They find legitimate projects from which they create a forked project. The malware is then hidden in the directory structure of that forked project. Using a phishing scheme, the cryptojackers lure people to download that malware through, for example, a warning to update their Flash player or the promise of an adult content gaming site.”
2. European bank case (2018)
In the beginning of the year, the European bank discovered suspicious server activity in its system. Although the security system did not discover any mistakes or invasions, the usual processes were performed slowly comparing to normal standards. Later it was discovered that some servers were showing up online at night although the bank stated that such servers did not exist. The inspection found the root of the threat: dishonest bank worker committed the insider crime through the installed a cryptomining system under the flooring.
What does this mean to you and your company?
Well, the accidentally opened cryptomining code harms the device performance through interfering with its system. Moreover, unlike other hacking methods, cryptojacking is silently stored in the computer and constantly harming the system with only a few noticeable infection signs.
However, here are a few things that serve as possible hints:
- A slowdown in device performance
- Overheated batteries
- Reduction in productivity
- Increased electricity usage expenses
Healthcare and banking institutions are mostly targeted by the cyber criminals. Especially, systems with old system settings are vulnerable to potential cryptojacking malware installation.
DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service)

Have you ever faced the problem of a webpage taking forever to get loaded or your favourite streaming/gaming platform being unavailable?

As it turns out, these may be caused by one of the top cyber security risks – a DDoS attack – which focuses on restricting legitimate users from accessing the website/system data. The hackers flood a network with random requests and information which “pollute” the system.
Why does this matter?
The accessibility is one of the key elements of the end-user experience.
Otherwise, the company whose products or services are not available to its customers risks undermining its credibility, or even losing some of the users.
Here is some stats from Kaspersky:
“The total number of attacks climbed by 84%, and the number of sustained (over 60 minutes) DDoS sessions precisely doubled. The average duration increased by 4.21 times, while the segment of extremely long attacks posted a massive 487% growth.”
Let’s look at some historical DDoS examples happened recently:
1. Imperva Clients (2019)
In January and then April, Imperva reported that their clients sustained 500 million and 580 million packets per second attacks respectively. The latter is considered the largest one by packet volume.
2. GitHub Case (2018)
Attack on GitHub had for some time been considered being the most massive one. In 2018 the system was overflowed with traffic which reached 1.35 terabits per second!
As reported by GitHub, over thousands of autonomous systems (Memcached servers) sent requests that exponentially increased the server traffic while the company security was not ready for such a massive scale attack. (The company had to seek DDoS mitigation from one of its security partners)
By the way, here’s what GitHub report stated:
“Over the past year we have deployed additional transit to our facilities. We’ve more than doubled our transit capacity during that time, which has allowed us to withstand certain volumetric attacks without impact to users…. Even still, attacks like this sometimes require the help of partners with larger transit networks to provide blocking and filtering”.
What does this mean to you and your company?
We won’t be wrong if we say that DDoS attacks threaten business development with long-run negative results.
“The total number of attacks climbed by 84%, while the segment of extremely long attacks posted a massive 487% growth.”
You might ask “What measures should business consider preventing DDoS then?”.
Even though it is not easy to protect against the Denial-of-Service attack, there are approaches that can improve your DDoS sustainability:
- Perform security evaluation to detect any DoS-related issues and develop a response plan.
- Establish strong security practices (especially on a network and application levels) and build redundancy.
- Utilize network monitoring controls to spot DDoS attacks and establish timely reporting procedures.
Conclusion:
Threats can come from anywhere, and it is our responsibility to develop a culture of cyber security.
More than ever it is important for organizations to approach cyber security measures with all seriousness.
It’s true that the cyber attackers’ methods evolve extremely fast developing news tools for accessing sensitive data or systems, or sabotaging those critical components for day-to-day business operations.
While it may seem to be expensive to manage security, the cost of idling could be exponentially higher.
But here is good news: you can be prepared for and even combat the majority of cyber security risks for your business.
Keep track of the cyber security updates and news. Reach out to security consulting for advice on how to best manage your systems and make those sustainable against cyber threats!


